Blended learning is an approach to education that combines online and face-to-face learning methods. There are different blended learning models depending on how the online and in-person components are integrated and balanced.
Blended learning is a growing trend in education. It aims to enhance student outcomes and satisfaction by providing more flexibility, personalization, and engagement in their learning process. Blended learning can be implemented in different forms. However, in general, the 4 most common models are the Rotation model (with 4 sub-models: Station rotation, Lab rotation, Individual rotation, and Flipped classroom), Enriched virtual model, Flex model, and A la carte model. Each model has its own advantages and challenges, and can be adapted to suit different contexts, goals, and students.
In this blog post, we will explore these types of blended learning in more detail. But where do you start? Traditional tools can be limited, and developing truly interactive material might seem daunting. This is where ActivePresenter comes in. ActivePresenter is a powerful, all-in-one eLearning authoring tool designed to make creating professional-quality online courses, software simulations, and interactive quizzes accessible and intuitive, even if you have no prior design or development experience. It’s the perfect partner for educators ready to build captivating learning materials that go beyond simple presentations.

1. Rotation Model
The rotation model is a type of blended learning that involves students rotating between different learning modalities on a fixed schedule, where at least one modality is online learning. The others can include group projects, individual tutoring, small-group instruction, or pencil-and-paper assignments. Students spend most of their learning time at school, except for homework assignments. The rotation model has four sub-models: station rotation, lab rotation, individual rotation, and flipped classroom.
1.1. Station Rotation
In this approach, students rotate through three types of stations: teacher-led, online, and offline. The number and duration of stations depend on the class size and period. A station can span more than one day or class. Students are required to rotate through all the stations.
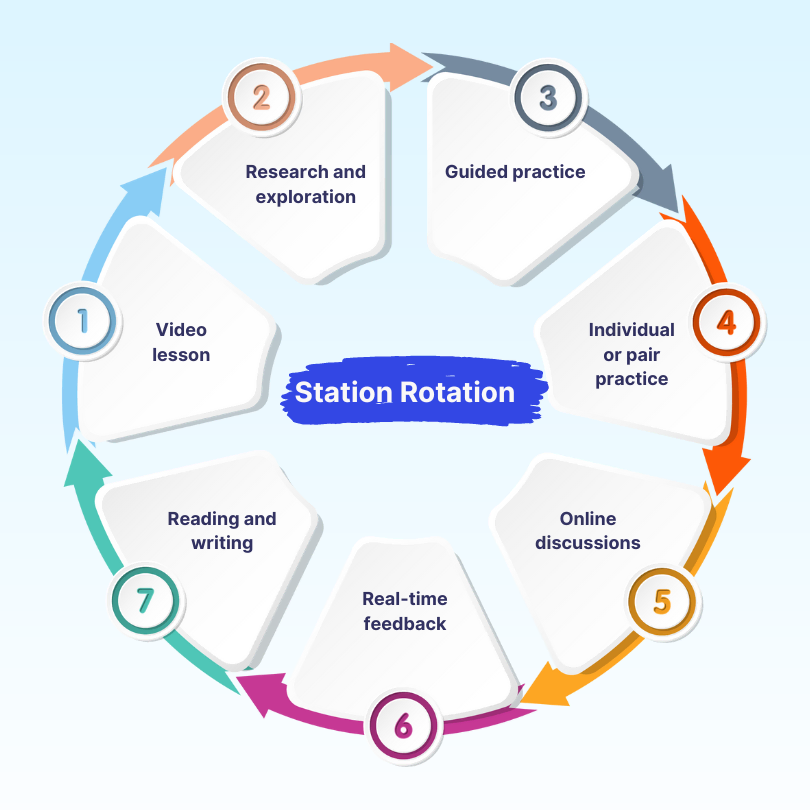
Key points:
- Schedule: Fixed schedule set by teachers
- Learning place: At school
- Learner’s role: Rotate through all stations
- Teacher’s role: Face-to-face support daily
1.2. Lab Rotation
This blended learning sub-model is similar to station rotation, but students rotate to a dedicated computer lab for the online learning station. This allows for more flexibility in classroom arrangements.
Key points:
- Schedule: Fixed schedule set by teachers
- Learning place: At school, but students have to rotate to a computer lab for the online learning section
- Learner’s role: Rotate to all stations
- Teacher’s role: Face-to-face support daily
1.3. Individual Rotation
This model is also known as the playlist rotation model. Students follow individualized schedules that are designed by teachers or software algorithms. Unlike station rotation, students do not need to rotate through all the stations, but only the ones on their playlist. This allows for more personalization and differentiation.
Key points:
- Schedule: Individualized schedule set by teachers or software algorithms
- Learning place: At school
- Learner’s role: Only rotate to stations on the playlist
- Teacher’s role: Face-to-face support on a daily basis
1.4. Flipped Classroom
The flipped classroom model is considered the most widely known blended learning model. It flips the traditional order of instruction and homework. Students must complete the coursework and lecture online at home using materials given by teachers. Then, teachers use class time for practice and feedback.

Key points:
- Schedule: Fixed schedule set by teachers
- Learning place: Learn coursework online at home and practice at school
- Learner’s role: Complete coursework at home online
- Teacher’s role: Face-to-face support daily
Besides, see Flipped Classroom Activity: Top 6 for Training Kids to learn more about the flipped classroom model.
2. Enriched Virtual Model
Enriched virtual is also a common blended learning model that combines online and face-to-face learning. Students must complete most coursework online, but have face-to-face sessions with teachers when required. Unlike the flipped classroom model, students don’t meet, and work with teachers on a daily basis. For example, some programs may require students to attend class only twice a week.
Key points:
- Schedule: Fixed schedule assigned by teachers
- Learning place: Learn online at home and practice at school
- Learner’s role: Complete coursework at home online
- Teacher’s role: Face-to-face support as needed
3. Flex Model
The flex model is a self-paced and student-driven model that allows students to follow a customized and flexible schedule based on their pace and needs. In this blended learning model, students mainly engage in learning activities in the digital environment at the school campus. For example, they participate in virtual classes on a learning management system (LMS) in the school computer lab. They study and practice new concepts independently. Teachers are onsite to provide face-to-face support as needed, such as small-group instruction, group projects, or individual tutoring.
Key points:
- Schedule: Customized and flexible schedule selected by students
- Learning place: At the school campus
- Learner’s role: Attend virtual class with remote teachers
- Teacher’s role: Provide onsite support as needed
To learn more about this model, see Flex Model: Definition, Benefits and Limitations.
4. A La Carte Model
This approach enables students to choose courses from a menu of a la carte options that suit their interests and needs. This model is useful when schools are unable to offer certain learning opportunities, such as gifted, elective, or advanced placement courses. By partnering with online course providers, schools can expand their offerings. Students can take online courses with a remote teacher at home or at school using technology support.

Key points:
- Schedule: Flexible and individual schedule decided by learners
- Learning place: At home or school depending on courses
- Learner’s role: Select courses from a menu of a la carte options
- Teacher’s role: Partner with course providers to expand the range of course options and provide face-to-face support in the traditional courses.
To learn more, see A La Carte Learning – A Fresh Perspective on Education.
So, you have learned about 4 common blended learning models. You can modify them to adapt to your training needs as well as student’s preferences. Thanks for reading. Besides, don’t forget to follow our Blog for more helpful articles.
See more: