The classic classroom is changing as we move into the digital age. Online learning is becoming more popular, leading to more adaptable and customized learning experiences. Two main models have appeared: synchronous vs asynchronous learning. Let’s examine the differences and benefits of each.
But first, do you know that you can create attractive eLearning courses using the powerful authoring tool called ActivePresenter? Believe me, whether you are approaching synchronous or asynchronous learning, this tool will be the best companion to help you create whatever content you need. So, download the app for free and experience it without any limitations now!

What is Synchronous Learning?
Synchronous learning refers to a network of unlimited learners involved in synchronous activities from different locations. In other words, this learning approach shows the interaction between instructors and learners in real time. Learners can attend live-broadcasted lectures and actively discuss them with the instructor and their peers at the same time.
Some examples of synchronous learning can be listed as:
- Virtual classrooms: Platforms like Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams.
- Live webinars: Platforms like YouTube Live or Webex.
- Collaborative group activities: Tools like Miro or Google Workspace with live video calls.
- Peer-to-peer learning sessions: Study groups on platforms like Discord, Slack, or Microsoft Teams .
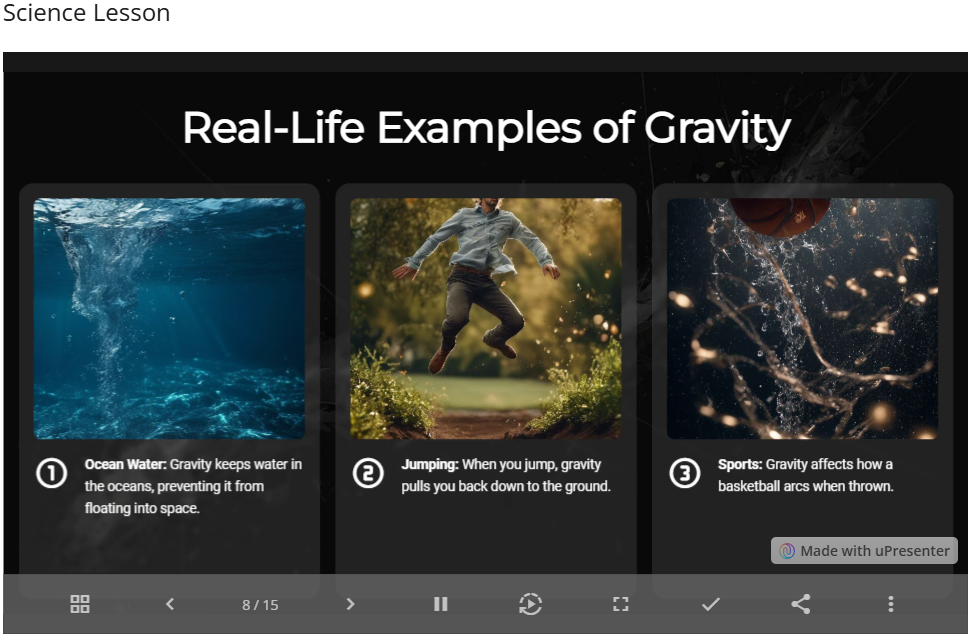
- Real-time testing or quizzes: Tool like uPresenter with real-time tracking.
Why Synchronous Learning?
Instant and active classroom interactions
The biggest benefit of synchronous learning is that learners can interact with professors and classmates actively and instantly during lectures. A real-time collaboration in learning could strengthen the learner’s knowledge absorption and increase learning outcomes. As a result, it can minimize the learning transaction distance.
Connection and communication
Since classes occur in real-time, learners have the opportunity to interact directly with their instructors and peers, resulting in more engaging and dynamic learning experiences. Communication with other learners also relieves learners from the feeling of isolation, thus keeping up their concentration and engrossment.
Motivation and accountability
Synchronous learning adheres to a fixed schedule, which makes learners more accountable for attending classes and submitting assignments on time. This sense of responsibility helps sustain motivation throughout the course. Moreover, knowing that class participation and attendance impact their grades or overall success, learners are less likely to procrastinate.
Immediate guidance and feedback
In synchronous learning, instructors are actively engaged in guiding the class, addressing questions, and offering valuable insights. That benefits learners in direct guidance, motivation, and support from instructors. Additionally, it enables instructors to adjust the pace or content based on the learners’ needs.
Does synchronous learning have any downside?
On the contrary, the timely lecture schedule poses a challenge for busy learners as they have to set aside a certain amount of time for attendance. Therefore, they had better check-up the timetable carefully before enrolling in.
What is Asynchronous Learning?
Nowadays asynchronous learning has become the most commonly-used type of learning. Its events and activities are time-independent, so learners can take courses or tests at their own place at any time. Asynchronous learning also facilitates learners to study offline with downloadable courseware. Different learners, therefore, may start and finish their courses asynchronously.
Examples of synchronous learning include:
- Self-paced online courses: Self-hosted LMS platforms like Moodle.
- Online forums and communities: LMS forums or Reddit communities.
- Recorded webinars: Webinars hosted on platforms like Zoom, YouTube, or a course’s LMS.
- eBooks and digital resources: PDF documents or Kindle-compatible books.
- Podcasts and audio learning: TED Talks Audio, Audible courses.
- eLearning courses with interactive content: eLearning authoring software like ActivePresenter that creates courses including multimedia content, simulations, drag-and-drop interactions, or gamified learning elements.

Why Asynchronous Learning?
Learn anytime, anywhere
Asynchronous learning allows learners to learn anywhere, anytime at their own pace. They may arrange their studying schedules on their own beyond the constraints of appointed lessons or periodical exams.
Personalized learning progress
An asynchronous learning approach places greater importance on learners’ cognitive benefits than the mere speed itself. With the adjustability of the timetable headed toward individual needs, learners can have time to reflect on what has been put across. They can have further research on the topic to ensure background information and get a better insight of the course.
Ideal for continuous learning
Asynchronous courses offer continuous access to learning materials, unlike traditional classrooms where lessons are temporary. Learners can revisit the content anytime, even after completing the course, to refresh and strengthen their understanding.
Cost effectiveness
Asynchronous online courses are typically more cost-effective than traditional classroom programs. Learners can avoid expenses such as commuting, housing, and other related costs. Similarly, institutions save on operational expenses, allowing them to offer courses at more affordable rate.
And Limitations of Asynchronous Learning?
Some people will find themselves too apathetic to finish the coursework without any deadline. Moreover, the humdrum contact in a one-way learning process with the computer may enervate learners, as a result, affect their outcomes.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous Learning: Choosing the Right Approach
To sum up, here is the comparison table between the synchronous vs asynchronous learning model:

The best approach often involves a blend of synchronous and asynchronous learning. By combining the benefits of both methods, instructors can create engaging and effective learning experiences.
See more: